In the processes of learning, change, and communication there are natural hierarchies, or logical levels. In logical levels you have sets and subsets. How the sets and subsets are logically set out.
Sometimes in NLP these levels are called Neurological levels as they reflect levels of thinking.
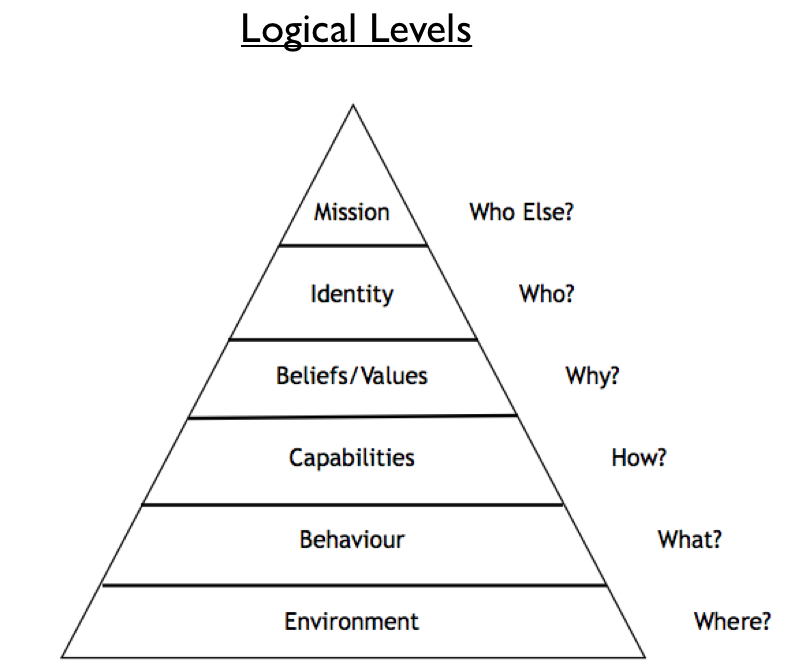
The function of each NLP logical level in the hierarchy is to organize the information below it. Changing something on a lower NLP logical level of the hierarchy could, but would not necessarily affect the levels above it. However… making a change at an upper level would necessarily change everything below it in order to support the higher level change.
Logical Levels of Change:
- Spirituality – Change for whom and/or what purpose?
- Identity – Does change reflect who I am?
- Values and beliefs– Why make the change?
- Capabilities and Skills- Change how?
- Behaviours – Change what?
- Environment – Where to change?
They are important for understanding change from an individual, social or organisational point of view. For desgining an action plan for change.
Using Neurological levels in NLP
Neurological Level help us understand the different levels at which we experience the world and at which level we should work to bring a change we desire.
We can help others by understanding at which level they are operating by listening to the language that they use. They might feel stuck in a problem because they are trying to find a solution but always operating on the same level. By helping them change their thinking to another level, we can bring them a new perspective for their problem.
This also applies to ourselves. By listening to the language used in our self-talk we can discover where the initial problem is being constructed and then address it in the right way.
First and Second Order Change
First Order Change
Change occurring on the same logical level as the problem state. Eg acting on behaviour to obtain a change in behaviour. Change in a specific behaviour in context. Anchoring.
Second Order Change
Any change which takes place at a higher logical level than the problem state. This allows the change to affect the system, thereby rendering the erstwhile problem harmless, irrelevant or useful. Change in an entire category of behaviours in context. Reframing.
This subject is covered in detail at our NLP Practitioner and NLP Master Practitioner Training Courses.
Logical Types
In logial levels there are 2 dimensions, the levels and the types within the levels. These are the types of things on a certain logical level. Eg different types of cars, within the set of cars.
This is important in order to develop flexibility in the client. Paying attention so that you know and understand where the client is chunking. Enables you to discover the clients true feelings.
